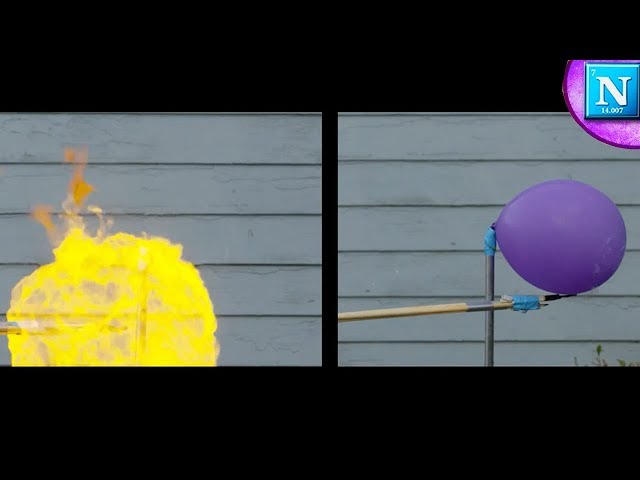A lot of people seem to think that oxygen is flammable. We’re here to set the record straight and tell you why that’s not the case!
Checkout this video:
What is oxygen?
Oxygen is a gas that makes up about 21% of the air (the rest is nitrogen and other gases). Oxygen is colorless, odorless, and tasteless. It is nonflammable and supports combustion. Because it is necessary for life, oxygen is often referred to as the elixir of life.
What is combustion?
Combustion is a rapid chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the generation of heat and light. In general, the fuel is a carbon-based material and the oxidant is oxygen from the air.
The word “flammable” means that something can be set on fire and will burn easily. So, if something is “incombustible,” it means it cannot be set on fire and will not burn.
While most people know that oxygen is essential for human life, few know that it is also one of the most abundant elements in the universe. Oxygen makes up about 21 percent of the air we breathe, and it is essential for combustion to occur.
In order for combustion to take place, three things are needed: fuel, heat and an oxidant. The most common type of fuel is a carbon-based material, such as wood, coal or natural gas Theheat can come from a match, lighter or sparks, and oxygen is necessary to complete the reaction.
Once these three elements are combined, the reaction occurs quickly, producing heat, light and often smoke.
While oxygen itself does not burn, it plays an important role in the burning process. When something burns, it combines with oxygen from the air to create new compounds.
For example, when wood burns, it combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water vapor.
What are the properties of oxygen that make it flammable?
User:Ana Maria Miguel
“Flammability” is defined as the ability of a substance to burn in air, often characterized by a flame or fire. The term most often refers to the ability of a fuel to sustain combustion, but it can also refer to the ability of an oxidizer to support the burning of a fuel.
A fuel is flammable if it can be ignited and will continue to burn in air. The fuel may be a solid, liquid or gas. An oxidizer is flammable if it will supply oxygen to support the burning of a fuel. The oxidizer may also be a solid, liquid or gas.
The ability of oxygen to support combustion is what makes it flammable. Oxygen is an oxidizer, meaning that it will supply oxygen to support the burning of a fuel. In order for combustion to occur, there must be both a fuel and an oxidizer present.
The flammability of oxygen can be demonstrated by placing a small amount of any combustible material, such as paper, in a sealed container such as a jar. Then add pure oxygen to the container until the paper is completely saturated with oxygen. Finally, seal the container so that no air can enter.
The paper will combust when exposed to any source of ignition, such as a match or spark. This demonstration shows that pure oxygen is flammable and will support combustion when combined with a fuel.
What are the conditions necessary for oxygen to combust?
In order for oxygen to combust, three conditions must be met: heat, fuel and an oxidizing agent.
Heat causes the molecules in the fuel to move faster, which makes it easier for them to react with the oxygen. The more heat that is present, the more quickly the reaction will occur.
The fuel must be able to react with oxygen in order to combust. Most common fuels are made up of hydrocarbons, which are molecules consisting of both hydrogen and carbon atoms.
The third ingredient needed for combustion is an oxidizing agent. This is a substance that can supply oxygen atoms to a reaction. The most common oxidizing agent is atmospheric oxygen, which is why most fires need air in order to continue burning.
When all three of these conditions are met, combustion will occur and the result will be fire.
What are the dangers of oxygen combustion?
While oxygen is not combustible, it supports combustion. That means that if you have a fire in an oxygen-rich environment, the fire will burn much more fiercely than it would in regular air. The high level of oxygen causes the fire to burn hotter and faster, which can be very dangerous.
What are some common myths about oxygen and combustion?
It’s a common misconception that oxygen is flammable. In fact, it’s impossible for oxygen to burn.
Here’s why: In order for something to burn, it needs three things: heat, oxygen, and fuel. The heat energy causes the molecules of the fuel to break apart and mix with the oxygen in the air. This mix then ignites, creating a chemical reaction that produces light, heat, and smoke.
Oxygen is essential for this chemical reaction to occur, but it doesn’t actually participate in the burning process — that’s why it can’t be considered flammable.
So what is oxygen if it isn’t flammable? It’s actually an oxidizer. That means that it helps other materials burn by providing the extra oxygen that they need to complete the chemical reaction.
While oxygen isn’t flammable, that doesn’t mean that it can’t be dangerous. If there is too much oxygen in an enclosed space, it can cause materials to burn more quickly than they otherwise would. This can create a fire hazard, which is why it’s important to use caution when using oxygen tanks or chambers.
What are some real-life examples of oxygen combustion?
While pure oxygen is not flammable, it greatly accelerates the burning process of other materials. In fact, many common materials will spontaneously burst into flame when they come into contact with pure oxygen at high pressures.
Some real-life examples of oxygen combustion include:
-The destruction of the Hindenburg airship: The Hydrogen gas that fueled the Hindenburg was not actually the main cause of the disaster — it was the oxygen in the air that caused the hydrogen to burn much more quickly than it normally would.
-The Apollo 1 launchpad fire: A fire broke out in the Apollo 1 spacecraft while it was still on the launchpad, and the pure oxygen atmosphere inside amplified the flames and killed the three astronauts onboard.
-The 1986 Space Shuttle Challenger disaster: A leak in one of the space shuttle’s boosters led to a fire that eventually caused the entire shuttle to explode. Again, it was the pure oxygen atmosphere that caused such rapid combustion.
How can the dangers of oxygen combustion be prevented?
While pure oxygen is not flammable, it is an extremely powerful oxidizer. This means that it facilitates the combustion of other materials. When oxygen is mixed with other materials, it can create a highly combustible mixture.
There are a few ways to prevent the dangers of oxygen combustion:
-Use appropriate ventilation: When using oxygen, be sure to have proper ventilation. This will help to disperse any combustible materials and reduce the risk of fire.
-Keep oxygen away from heat sources: Avoid using oxygen near anything that could create a spark or heat source. This includes cigarettes, matches, lighters, and electrical equipment.
-Do not smoke: Smoking is one of the most common causes of fires in oxygen-enriched environments. If you must smoke, do so only in designated smoking areas and with proper precautions.
-Be aware of potential risks: Be mindful of the potential hazards of working with oxygen. combusted Use caution and follow all safety guidelines when handling this gas.
What are the implications of oxygen combustion?
While oxygen is not flammable itself, it is required for combustion to occur. In other words, oxygen facilitates and supports fire. When there is too little oxygen present, firefighters say that the fire has been “starved” of oxygen and it will go out.
What are the future research directions for oxygen combustion?
There is still much to learn about the role of oxygen in combustion, and future research directions will likely focus on a better understanding of how different oxygen concentrations can impact the rate and intensity of a fire. Additionally, research may also focus on how to best control oxygen levels in order to optimize fire performance.